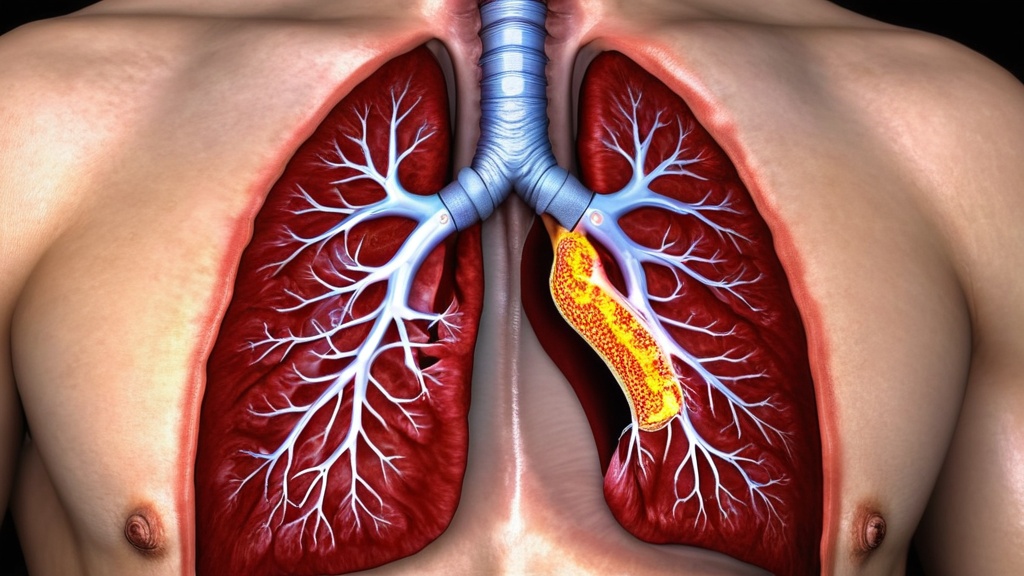
Lung cancer is one of the most prevalent cancers globally. It develops when malignant cells in the lungs multiply uncontrollably and form tumors. These tumors can impair normal respiratory function and metastasize to other organs and tissues throughout the body.
Lung cancer is classified into two primary categories: non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC). NSCLC represents approximately 85% of all diagnosed cases and is the more common form. Lung cancer typically develops over an extended period, making early detection essential for improved treatment outcomes.
Multiple factors contribute to its development, including genetic predisposition, environmental exposures, and lifestyle behaviors. Awareness of lung cancer risk factors and disease progression enables individuals to prioritize health monitoring and seek appropriate medical evaluation when symptoms or concerns arise.
Key Takeaways
- Lung cancer risk is increased by factors like smoking and environmental exposures.
- Early symptoms include changes in breathing, persistent cough, and chest discomfort.
- Unexplained weight loss, fatigue, hoarseness, and wheezing can signal lung cancer.
- Early detection significantly improves treatment outcomes and survival rates.
- Prompt medical consultation and screening are crucial for at-risk individuals.
Common Risk Factors for Lung Cancer
Several risk factors contribute to the likelihood of developing lung cancer. Smoking remains the leading cause, responsible for approximately 85% of cases. Even secondhand smoke poses a significant risk to non-smokers.
For instance, a person living with a smoker may inhale harmful chemicals, increasing their chances of developing lung cancer. Other risk factors include exposure to radon gas, asbestos, and certain chemicals like arsenic and diesel exhaust. Individuals working in industries such as construction or mining may face higher exposure levels.
Additionally, a family history of lung cancer can increase one’s risk, highlighting the importance of genetic factors in this disease.
Early Signs and Symptoms of Lung Cancer
Recognizing early signs and symptoms of lung cancer can significantly impact treatment outcomes. Many people may not experience noticeable symptoms in the initial stages. However, being aware of subtle changes in your body can lead to earlier diagnosis and intervention.
Common early symptoms include persistent coughing, changes in breathing patterns, and unexplained weight loss. If you notice any of these signs, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation. Early detection can lead to more effective treatment options and better survival rates.
Changes in Breathing Patterns
Changes in breathing patterns can be an early indicator of lung cancer. You might notice shortness of breath during activities that previously felt easy. For example, climbing stairs may become more challenging than it used to be.
This change can occur due to a tumor obstructing airways or fluid buildup in the lungs. If you find yourself feeling breathless without a clear reason, it’s important to seek medical advice. A healthcare provider can assess your symptoms and determine if further testing is necessary.
Early intervention can help address potential issues before they escalate.
Persistent Coughing
| Early Sign | Description | Commonality | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Persistent Cough | A cough that does not go away or worsens over time | Very Common | Often mistaken for a cold or bronchitis |
| Coughing up Blood | Presence of blood in sputum or phlegm | Common | Requires immediate medical evaluation |
| Shortness of Breath | Difficulty breathing or feeling breathless | Common | May indicate tumor obstruction or fluid buildup |
| Chest Pain | Discomfort or pain in the chest area | Moderate | Can worsen with deep breathing or coughing |
| Hoarseness | Changes in voice or hoarse voice | Less Common | May result from nerve involvement |
| Unexplained Weight Loss | Significant weight loss without trying | Moderate | Often a late sign but can appear early |
| Fatigue | Persistent tiredness or lack of energy | Common | Non-specific symptom but important to note |
| Recurrent Respiratory Infections | Frequent episodes of bronchitis or pneumonia | Moderate | May indicate impaired lung function |
A persistent cough is one of the most common symptoms associated with lung cancer. Unlike a typical cough that resolves within a few weeks, a cough related to lung cancer may last for an extended period or worsen over time. For instance, you might start with a mild cough that gradually becomes more frequent and severe.
If you experience a cough that doesn’t improve or is accompanied by other symptoms like blood in your sputum, it’s crucial to consult a doctor. They can perform tests to determine the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment options if necessary.
Chest Pain and Discomfort
Chest pain or discomfort can also signal potential lung issues, including lung cancer. This pain may feel sharp or dull and can occur during deep breaths or coughing. For example, you might feel a nagging ache in your chest that intensifies when you take a deep breath.
While chest pain can result from various conditions, it’s essential not to ignore it, especially if it persists or worsens over time. A healthcare professional can evaluate your symptoms and conduct tests to rule out serious conditions like lung cancer.
Unexplained Weight Loss
Unexplained weight loss is another symptom that may indicate lung cancer or other serious health issues. If you notice significant weight loss without changing your diet or exercise routine, it’s worth discussing with your doctor. For instance, losing 10 pounds over a few months without trying could be a red flag.
Weight loss can occur due to the body’s increased energy demands when fighting cancer or due to decreased appetite. Early detection is vital for effective treatment, so don’t hesitate to seek medical advice if you experience this symptom.
Fatigue and Weakness
Fatigue and weakness are common complaints among individuals with lung cancer. You might feel unusually tired even after a full night’s sleep or find it challenging to complete daily tasks. For example, you may struggle to keep up with your usual activities, like walking the dog or doing household chores.
This fatigue can stem from various factors, including the body’s response to cancer or anemia caused by the disease. If you experience persistent fatigue that interferes with your daily life, consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and support.
Hoarseness and Wheezing
Hoarseness and wheezing are additional symptoms that may indicate lung cancer. Hoarseness occurs when the vocal cords are affected by nearby tumors or inflammation. You might notice your voice sounding raspy or strained, which can be concerning.
Wheezing is characterized by a high-pitched whistling sound during breathing, often caused by narrowed airways. If you experience these symptoms alongside others like coughing or shortness of breath, it’s essential to seek medical attention promptly.
Recognizing the Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of lung cancer significantly improves treatment outcomes and survival rates. Regular check-ups and awareness of symptoms can help catch the disease in its initial stages when it is most treatable. For instance, individuals at high risk due to smoking or family history should consider discussing screening options with their healthcare provider.
Screening methods like low-dose computed tomography (CT) scans have shown promise in detecting lung cancer early in high-risk populations. The American Cancer Society recommends annual screening for adults aged 55 to 80 who have a history of heavy smoking.
Seeking Medical Help and Screening Options
If you notice any concerning symptoms related to lung cancer, don’t hesitate to seek medical help. A healthcare professional can conduct a thorough evaluation and recommend appropriate tests based on your symptoms and risk factors. This may include imaging tests like X-rays or CT scans, as well as biopsies if necessary.
For those at higher risk, discussing screening options is crucial. Low-dose CT scans can detect lung cancer at earlier stages than traditional X-rays. Engaging in open conversations with your healthcare provider about your concerns can lead to timely interventions and better health outcomes.
In conclusion, understanding lung cancer and its risk factors is essential for early detection and effective treatment. By recognizing symptoms such as persistent coughing, changes in breathing patterns, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, hoarseness, and chest pain, individuals can take proactive steps toward their health. Regular check-ups and open communication with healthcare professionals play vital roles in managing risks associated with lung cancer.
FAQs
What are the early signs of lung cancer?
Early signs of lung cancer can include a persistent cough, coughing up blood, chest pain, shortness of breath, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and recurrent respiratory infections such as bronchitis or pneumonia.
How soon do symptoms of lung cancer appear?
Symptoms of lung cancer may not appear until the disease is advanced. Early-stage lung cancer often has no noticeable symptoms, which is why regular screenings are important for high-risk individuals.
Can a cough be a sign of lung cancer?
Yes, a persistent cough that does not go away or worsens over time can be an early sign of lung cancer, especially if it is accompanied by other symptoms like coughing up blood.
Is shortness of breath an early symptom of lung cancer?
Shortness of breath can be an early symptom of lung cancer, particularly if the tumor blocks airways or causes fluid to build up around the lungs.
Are there any non-respiratory early signs of lung cancer?
Yes, non-respiratory early signs can include unexplained weight loss, fatigue, hoarseness, and swelling in the face or neck due to blocked blood flow.
Who is at higher risk for developing lung cancer?
People who smoke or have a history of smoking, those exposed to secondhand smoke, radon gas, asbestos, or other carcinogens, and individuals with a family history of lung cancer are at higher risk.
How is lung cancer diagnosed if early signs are present?
If early signs are present, doctors may perform imaging tests such as chest X-rays or CT scans, followed by biopsy procedures to confirm the diagnosis.
Can early detection of lung cancer improve treatment outcomes?
Yes, early detection of lung cancer significantly improves treatment options and outcomes, making regular screenings important for high-risk individuals.
Should I see a doctor if I experience symptoms like a persistent cough or chest pain?
Yes, it is important to consult a healthcare professional if you experience persistent respiratory symptoms or other signs associated with lung cancer for proper evaluation and diagnosis.